HMG CoA reductase inhibitors - INTRODUCTION
The action and use of statins by Dr Angelo Pieris. Teaching Fellow in Clinical Pharmacology and Prescribing. Barts & The London Medical School.
Updated by Dr Hew Torrance, July 2013.
Aim: You will learn the practical therapeutic knowledge to appropriately prescribe this drug, including being aware of adverse interactions.

Why do I need to know about statins?
There are several reasons:
You need to be aware there are several pharmacological means of lowering cholesterol, without knowing detailed mechanisms.
What is a statin?
(Have a look at the "Mode of Action" page)
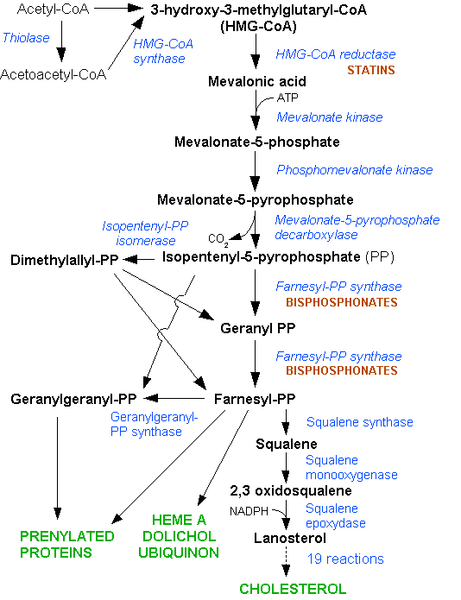
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors - MODE OF ACTION
Which is the lipid that is the "healthy" one amongst the two "unhealthy lipids" listed below?
I thought not eating cholesterol rich food such as eggs was an effective means of lowering cholesterol, why is it not?
The liver produces most of the cholesterol found in the body. It is not just absorbed from the gut and then passed around the bloodstream.
Statins work on the liver, disrupting this pathway of cholesterol synthesis.
Liver cells compensate for the lack of cholesterol production by increasing their uptake of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. This reduces circulating levels of LDL cholesterol.
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors - INDICATIONS
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has produced guidance indicating which patient groups stand to benefit from statin therapy.
The cornerstones of the guidance are;
Which of the three patients below do you think has the highest risk of a cardiovascular event based on the information given?
Where you suspect that an asymptomatic patient may have an increased risk or cardiovascular diasease, such as in a primary care setting what should you do?
NICE guides us to formally calculate the 10 year risk of cardiovascular events for the particular patient based on their risk factors.
This is then related to studies of populations and the rates of cardiovascular disease over time.
One example of this is the FRAMINGHAM model from the USA, and ASSIGN from Scotland.
So how many Bangladeshi men with type II diabetes living in Whitechapel does the FRAMINGHAM model have evidence for?
Good question; The answer is that it does not include this population, so clinical judgement needs to be applied. Equally it has been found that the model over-calculates risk for affluent white Europeans.
A 10 year risk is calculated to assist in decisions regarding the use of statins.
The risk factors for an increased chance of suffering from myocardial infarction, angina, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease should roll of your tounge. in every history and patient encounter relevant to this issue.... What are they?
Non-modifiable:
Gender (male worse), Ethnicity (South Asian worse), Age (older worse), Genetic disease (Familial hypercholesterolaemia), type II diabetes,
Modifiable (Some are very difficult to actually change for individual people)
Socio-economic class (deprived worse), alcohol consumption (binge drinking and over limits consumption worse), physically activity (inactive worse), smoking (worse), diet (high saturated fat worse)
Blood pressure (diet, activity, weight and medications can modify this), Extremes of weight (i.e anorexia, high central obersity).
How do I calculate a 10 year risk?
Google for a cardiovascular risk calculator using keywords, or look at the BNF where there are colour tables.
GPs often have computer software that can do this based on information already in the patient's record.
NICE have recommended that giving a statin (e.g. Simvastatin 40mg at night) should be considered for asymptomatic patients as a primary preventative (i.e. before any actual event has been recorded) measure with a 10 year cardiovascular risk greater than ...% (Have a guess and look at the feedback)
Patients who have suffer from established cardiovascular disease should be offered a statin, such as starting with simvastatin 40mg, and it is now recommended that patients with acute coronary syndrome should be treated with a higher intensity dose statin, e.g. simvastatin 80mg at night.
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors - PRESCRIBING
To summarise from the previous page:
Case
Mrs Kneebone was admitted to hospital recently with chest pain and diagnosed with a non ST segment myocardial infarction. She was already on treatment for rhumatoid arthritis, and was given a raft of new cardioprotective medications before being discharged from hospital. (Can you remember what they were? See "Drug of the week" on ACE inhibitors)
What lipid management therapy would you give Mrs Kneebone before discharging her from the acute/coronary care ward?
Why prescribe simvastatin? The drug company rep that paid for my lunch said that another statin is better!
This is because simvastatin...
Mrs Kneebone had a full set of blood tests when she was admitted to hospital. Which two should you definitely look at before starting a statin?
When Mrs Kneebone is being discharged, you are asked to help her hospital doctor write her discharge summary that will be sent to her GP.
NICE states that LFTs should be checked within 3 monts of starting, and then at 1 year, and not again if no problems have been encountered.
What if Mrs Kneebone were to ask "Doctor I am on an awful lot of medications, what are the side effects of this Statin that you have given me?"
You need to be aware of the common, and uncommon but potentially dangerous:
Mrs Kneebone comes to the GP practice a month later complaning of terrible pains in her leg and arm muscles.
What is the most appropriate course of action?
Mrs Kneebone's blood tests were normal, but the cramps did subside when the statin was stopped.
You decide to prescribe Pravastatin another HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) but from a different brand/type.
To minimise side effects the GP prescribes a low dose, and then builds this up.
What is one of the differences between brands such as simvastatin and atorvastatin and pravastatin?
Pravastatin is metabolized by a different pathway (i.e. not P450)
Is there not a simple level above which people should be treated with a statin?
NICE underlines using cardiovascular risk assessment. This should be done with all patients who youthink might benefit from a statin. In a scenario where the patient had a risk of less than 20% but a total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio of greater than 6 you could treat with a statin.
What level of cholesterol should treatment be targeted at?
In high risk patients aim for a total cholesterol of less than 4, but be aware that this may not be reached.
Which is the most accurate summary of cholesterol levels as a risk factor?
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors - INTERACTIONS
Many of the statins, especially simvastatin, are metabolized by the enzyme pathway in the liver CYP450.
Anything that is given to a patient that can alter this pathway, such as slowing it down, can alter the level of statin in the body.
Does this matter?
Yes because statins' adverse effects are dose related.
So what is the effect of inhibiting CYP450 enzyme metabolism?
The effective dose of the statin is increased.
So what can affect CYP450?
Several things, such as macrolide antibiotics, antifungal drugs and grapefruits.
A patient is admitted and treated for community acquired pneumonia with clarithromycin (a macrolide) and amoxicillin. They are normally on 80mg of Simvastatin.
What should you do to avoid a drug interaction whilst treating the patient to best effect?
Sometimes statins are given together with an other lipid lowering class of drug called Fibrates. In such cases the risk of myopathy is increased several-fold.
Anyone with rhabdomyolysis from what ever cause should have their statin stopped whilst they are being treated.
Bibliography:
National Institute for Clinical Excellence and Health. Clinical Guideline 67 Lipid Modification. Reissued march 2010.
Richards, D. Aronson, J. Oxford Handbook of Practical Drug Therapy. OUP 2005